vier bene hoekyster / buis kommunikasie torings
Januarie 12, 2019
Riglyne oor Tegniese Spesifikasies Kommunikasie toring
Januarie 21, 2019Ontleding van Geankerde staal traliemas blootgestel aan die omgewing baie
Ontleding van Geankerde staal traliemas blootgestel aan die omgewing baie
Staal rooster maste rang onder die mees doeltreffende draers strukture op die gebied van hoë konstruksie. Die nie-lineêre analise van 'n Geankerde staal traliemas gedoen word met behulp van die SAP 2000 eindige-element-program vir verskillende ys dikte waardes by 1500 m van hoogte bo seespieël. Na definisie van die geometriese model en kruis- artikel eienskappe, verskeie load kombinasies ontleed. uiteindelik, die wind spoed- ys dikte verhouding verkry, en die maksimum spoed wind wat die struktuur kan weerstaan, word bepaal vir verskillende ys diktes.
- inleiding
Traliemas is 'n algemene naam vir verskillende soorte staalmaste. 'n Traliemas of vakwerkmas is 'n vrystaande raamwerkmas. Hierdie strukture kan veral vir transmissiemaste gebruik word
spannings van meer as 100 kilovolt, as radiomaste (self-straal maste of draers vir antennes), of as waarnemingsmaste vir veiligheidsdoeleindes. Groot en swaar raamgedeeltes word nie hierin vereis nie
maste. Dit is hoekom hulle ligter is as ander masttipes, en die modules kan maklik aan mekaar gekoppel word.
Staalroostermaste word al vir baie jare gebruik in die lande waar die ys- en windladings aansienlik is. Dit is te wyte aan toenemende eise van die moderne industrie met betrekking tot kommunikasie en energie. Daar is verskillende style van maste waarop klein windkragopwekkers gemonteer is: vrye staande, gekartelde traliewerk, en kantel op. Vrystaande maste is relatief swaardiens, en hulle bly regop sonder die hulp van ou kabels. Gestampte traliemaste gebruik insteekkabels om die mas te anker en dit regop te hou met 'n relatief klein hoeveelheid beton. Kabels strek van drie punte naby die bokant van die mas tot by die grond op 'n afstand van die basis van die mas. Hierdie konstruksies is redelik lig in vergelyking met vrystaande maste, en vorm dus die goedkoopste manier om 'n windturbine te ondersteun. Maar, hulle benodig 'n groter area om die kabels te akkommodeer.
Die tegniese doeltreffendheid en duursaamheid van staalroostermaste het die afgelope jaar toegeneem. Die gedrag van staalroostermaste is in literatuur ondersoek. Aangesien die ontwerpprosedure betekenisvol is in hierdie maste, die struktuuranalise hou verband met die geometriese model en snit-eienskappe. so, die moduleproduksie- en monteringstappe, en ekonomiese koste, hou direk verband met die ontwerp van maste. Staalroostermaste op land is kwesbare strukture. Hulle word meestal deur omgewingsbelading geraak. Windvragte is die doeltreffendste ontwerpkriteria vir hierdie strukture. Maar, die ys-effek moet ook in ag geneem word, veral op hoë hoogtes. In koue streke, hierdie twee effekte word gekombineer. daarom, die verband tussen die wind en ys moet ondersoek word deur behoorlike eindige-element-ontledings uit te voer om die ineenstorting van sulke strukture te vermy. In hierdie dokument, die nie-lineêre analise van 'n gewelfde staal traliemas 80 m in hoogte word uitgevoer met behulp van die SAP 2000 program. Terwyl die model volgens TS saamgestel is 648 lastoestande word van TS geneem 498. Die hoogte van die struktuur word aangeneem 1500 m, en die sneeustreek IV word aangeneem, wat die mees konserwatiewe opsie is. Op hierdie manier, die ontleding kan ook vir ander sneeustreke gebruik word. Die struktuur is eers ontleed sonder enige ys-effek. Daarna, die ysdikte is geleidelik vergroot, en die verband tussen die windspoed en ysdikte is bepaal.
- Materiaal en metode
Die regte seksies en hoeke van die staalroostermas word eers bepaal. Daarna, die driedimensionele eindige elementmodel word in Figuur gegee 1. Boaansig van die model word aangebied
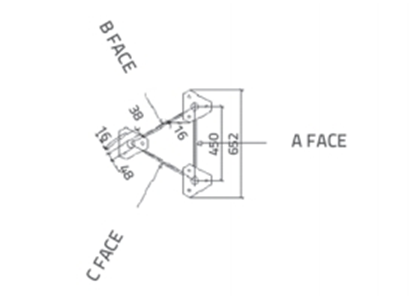
in Figuur 2. Gesiggedeeltes van die model, wys die afstande met hoeke, word in figuur getoon 3 en Figuur 4.
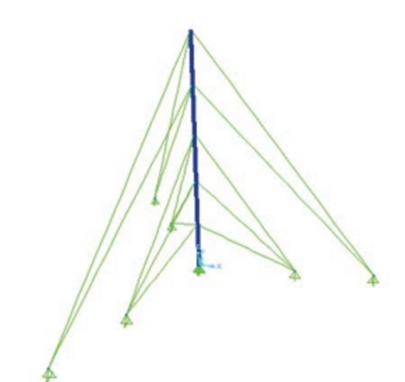
Figuur 1. 3-D model
Figuur 2. Top beskou
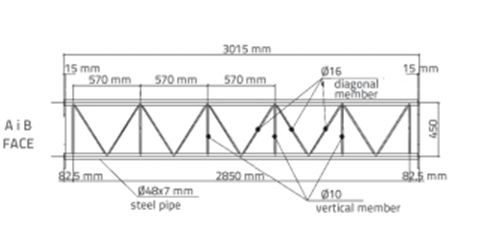
Figuur 3. A en B gesig artikels
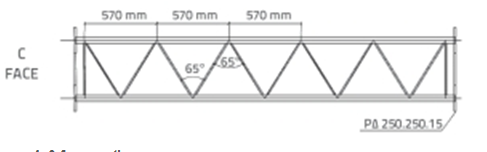
Figuur 4. C gesig artikel
tafel 1. materiaal eienskappe
|
materiaal tipe |
trek krag [MPa] |
opbrengs krag [MPa] |
|
St52 (S355) |
510 |
360 |
tafel 2. artikel eienskappe
|
lid tipe |
artikel tipe |
grootte [mm] |
|
kolom lede |
pyp |
48×7 |
|
vertikale lede |
omsendbrief |
16 |
|
diagonale lede |
omsendbrief |
16 |
|
Guy lede |
omsendbrief |
16 |
tafel 3 Windspoed en vele volgens hoogte
|
Hoogte [m] |
wind spoed “v” [m / s] |
wind vrag “q” 2 [kg / m ] |
|
0-8 |
28 |
50 |
|
8-20 |
36 |
80 |
|
20-80 |
46 |
130 |
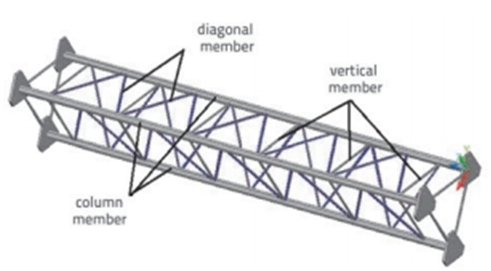
'n Module 3015 mm in lengte is gemaak van staallede. Kolomme word geplaas teen 'n hoek van 900 grond toe. Vertikale staallede verbind kolomme met mekaar, en word vertikaal geplaas met betrekking tot die kolomme. Diagonale lede word deur bepaalde hoeke na die kolomme geplaas, en hulle verbind ook die kolomme met mekaar. 'n Kolom met diagonale en vertikale lede wat die module uitmaak, word in figuur getoon 5.
Figuur 5. module lede
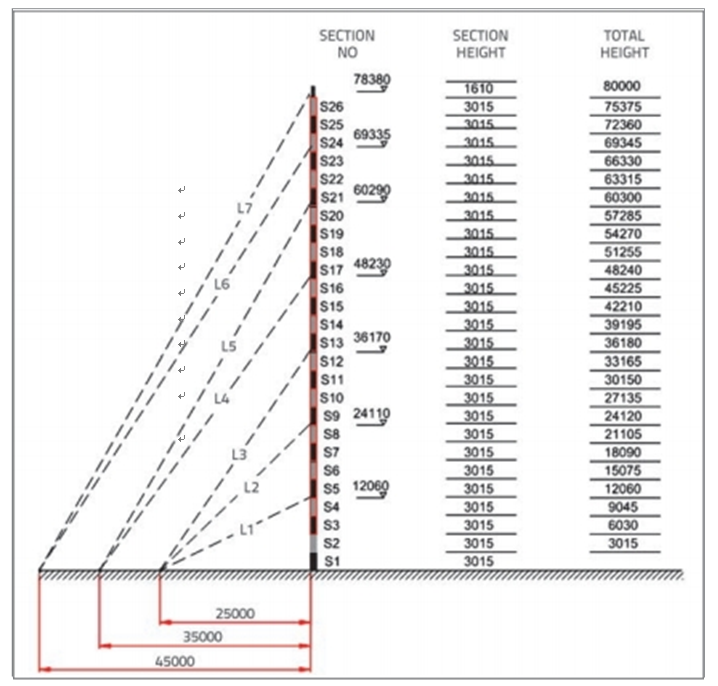
Guylede en modules word benoem volgens die totale hoogte vanaf die grondvlak. Die ou en seksie nommers, met verwante hoogtes, word in figuur aangebied 6.
tafel 4. Hoogte en sneeu eienskappe
|
Hoogte [m] |
sneeu streek |
sneeu vrag qs 2 [kg / m ] |
|
1500 |
IV |
176 |
tafel 5. Ys eienskappe
|
gewig van eenheid volume [kN / mm ³ ] |
|
7 |
Daar is 26 modules in die mas. die kolom, vertikale,en skuins lede in elke vlak van die module is shownin figuur 7. Positiewe en negatiewe windrigtings wat die
module word ook aangebied in die figuur.

tafel 6 artikel eienskappe
|
lid |
artikel tipe |
artikel grootte [mm] |
artikel omtrek [cm] |
artikel gebied 2 [cm ] |
|
kolom |
pyp |
48×7 |
15.08 |
9.02 |
|
vertikale |
omsendbrief |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
diagonale |
omsendbrief |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
Guy |
omsendbrief |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
kolom |
pyp |
48×7 |
15.08 |
9.02 |
|
vertikale |
omsendbrief |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
diagonale |
omsendbrief |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
Guy |
omsendbrief |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
kolom |
pyp |
48×7 |
15.08 |
9.02 |
|
vertikale |
omsendbrief |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
diagonale |
omsendbrief |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
Guy |
omsendbrief |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
kolom |
pyp |
48×7 |
15.08 |
9.02 |
|
vertikale |
omsendbrief |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
diagonale |
omsendbrief |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
Guy |
omsendbrief |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
Laskombinasies wat in die analise gebruik word, word in Vgl (1) en Vgl (2) soos volg. Die kombinasies word saamgestel deur sneeuvragte, ysladings volgens ysdiktewaardes,
en windbelasting wat verskillende hoogtes van die traliemas met windsnelhede bewerkstellig, word in tabel gegee 7.
|
lid |
sneeu vrag 2 [kg / m ] |
versprei sneeu vrag [kg / m] |
Ys dikte [mm] |
versprei ys vrag [kg / m] |
wind spoed [km / h] |
wind vrag volgens om hoogte [kg / m] |
||
|
0-8 m |
8-20 m |
20-80 m |
||||||
|
kolom |
176 |
- |
30 |
5.15 |
209 |
12.18 |
19.49 |
26.81 |
|
vertikale lid |
4.42 |
3.03 |
4.06 |
6.50 |
8.94 |
|||
|
diagonale lid |
4.42 |
3.03 |
4.06 |
6.50 |
8.94 |
|||
|
Guy |
4.42 |
3.03 |
4.06 |
6.50 |
8.94 |
|||
|
kolom |
176 |
- |
20 |
2.99 |
217 |
12.63 |
20.21 |
27.79 |
|
vertikale lid |
4.42 |
1.58 |
4.21 |
6.74 |
9.26 |
|||
|
diagonale lid |
4.42 |
1.58 |
4.21 |
6.74 |
9.26 |
|||
|
Guy |
4.42 |
1.58 |
4.21 |
6.74 |
9.26 |
|||
|
kolom |
176 |
- |
10 |
1.28 |
223 |
12.96 |
20.73 |
28.50 |
|
vertikale lid |
4.42 |
0.57 |
4.32 |
6.91 |
9.50 |
|||
|
diagonale lid |
4.42 |
0.57 |
4.32 |
6.91 |
9.50 |
|||
|
Guy |
4.42 |
0.57 |
4.32 |
6.91 |
9.50 |
|||
|
kolom |
176 |
- |
0 |
- |
226 |
13.14 |
21.03 |
28.92 |
|
vertikale lid |
4.42 |
- |
4.38 |
7.01 |
9.64 |
|||
|
diagonale lid |
4.42 |
- |
4.38 |
7.01 |
9.64 |
|||
|
Guy |
4.42 |
- |
4.38 |
7.01 |
9.64 |
|||
load-effekte lateraal lede. Versprei sneeu vrag word bereken deur die oorweging van top oppervlakte van die lede.
Verwante poste
'N Kommunikasietoring is 'n tipe seinoordragtoring, ook bekend as 'n seinoordragtoring of kommunikasie-ystertoring. In die konstruksie van moderne kommunikasie- en radio- en televisieseinoordragtorings, ongeag of gebruikers grondvlak of ystertorings op die dak kies, Hulle speel almal 'n rol in die verhoging van kommunikasie-antennas, die verhoging van die diensradius van kommunikasie- of televisie-transmissieseine, en die bereiking van ideale gespesialiseerde kommunikasie-effekte. Daarbenewens, Die dak speel ook 'n dubbele rol in weerligbeskermingsgronding, roete waarskuwing, en versiering van kantoorgeboue.









