четыре ноги угла башни железа / трубка связи
январь 12, 2019
Руководство по техническому спецификации башни связи
январь 21, 2019Анализ вантовой стальной решетки мачты подвергается нагрузкам на окружающую среду
Анализ вантовой стальной решетки мачты подвергается нагрузкам на окружающую среду
Стальные решетчатые мачты место среди наиболее эффективных несущих конструкций в области высотного строительства. Нелинейный анализ вантовой стальной решетки мачты осуществляется с использованием SAP 2000 конечных элементов программы для различных значений толщины льда в 1500 м высоты. После определения геометрической модели и крест- раздел свойства, различные комбинации нагрузок анализируются. Окончательно, скорость ветра- Отношение толщины льда получается, и максимальная скорость ветра, что структура может выдержать определяется для различной толщины льда.
- Вступление
Решетчатая мачта — это общее название различных видов стальных мачт. Решетчатая мачта или ферменная мачта представляет собой отдельно стоящую каркасную мачту.. Эти конструкции могут использоваться в качестве передающих мачт, особенно для
напряжения более 100 киловольт, как радиомачты (самоизлучающие мачты или держатели для антенн), или в качестве наблюдательных мачт в целях безопасности. В этих моделях не требуются большие и тяжелые секции рамы.
мачты. Вот почему они легче других типов мачт., и модули легко соединяются друг с другом.
Стальные решетчатые мачты уже много лет используются в странах со значительными ледовыми и ветровыми нагрузками.. Это связано с возрастающими требованиями современной промышленности к связи и энергетике.. Существуют разные стили мачт, на которых крепятся небольшие ветрогенераторы.: отдельно стоящий, вантовая решетка, и наклон вверх. Отдельно стоящие мачты рассчитаны на относительно тяжелые условия эксплуатации., и они остаются в вертикальном положении без помощи растяжек. В решетчатых мачтах с оттяжками используются оттяжки для крепления мачты и удержания ее в вертикальном положении с использованием относительно небольшого количества бетона.. Тросы тянутся от трех точек возле вершины мачты до земли на некотором расстоянии от основания мачты.. Эти конструкции достаточно легкие по сравнению с отдельно стоящими мачтами., и, следовательно, представляют собой наименее дорогостоящее средство поддержки ветряной турбины.. Однако, им требуется большая площадь для размещения растяжек.
Техническая эффективность и долговечность стальных решетчатых мачт за последние годы возросли.. Поведение стальных решетчатых мачт исследовалось в литературе.. Поскольку в этих мачтах важна процедура проектирования, структурный анализ связан с геометрической моделью и свойствами сечения.. таким образом, этапы производства и сборки модуля, и экономические затраты, напрямую связаны с конструкцией мачт. Стальные решетчатые мачты на суше являются уязвимыми конструкциями. Больше всего на них влияет экологическая нагрузка. Ветровые нагрузки являются наиболее эффективным критерием проектирования этих конструкций.. Однако, ледяной эффект также необходимо учитывать, особенно на больших высотах. В холодных регионах, эти два эффекта сочетаются. Следовательно, взаимосвязь между ветром и льдом должна быть исследована путем проведения надлежащего анализа методом конечных элементов, чтобы избежать обрушения таких конструкций.. В этой статье, нелинейный анализ стальной решетчатой мачты с оттяжками 80 м по высоте выполняется с использованием SAP 2000 программа. Хотя модель составлена по ТС 648 условия нагрузки взяты из TS 498. Высота конструкции принимается равной 1500 м, и принят снежный регион IV, это самый консервативный вариант. Таким образом, анализ также может быть использован для других снежных регионов.. Структура была впервые проанализирована без какого-либо эффекта льда.. После, толщина льда постепенно увеличивалась, и была определена связь между скоростью ветра и толщиной льда..
- Материал и метод
Сначала определяются правильные сечения и углы стальной решетчатой мачты.. После, трехмерная конечно-элементная модель представлена на рисунке. 1. Представлен вид модели сверху.
на рисунке 2. Лицевые части модели, показывая расстояния с углами, показаны на рисунке 3 и рисунок 4.
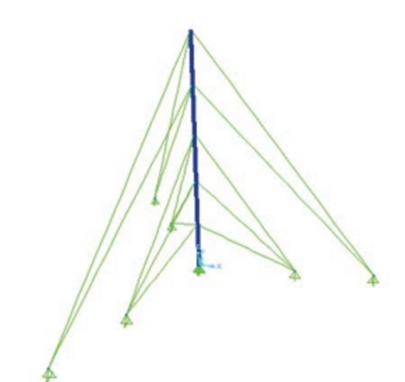
Фигура 1. 3-D модель
Фигура 2. верхний Посмотреть
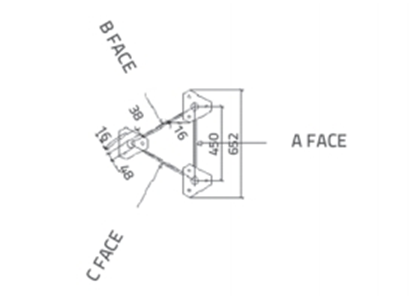
Фигура 3. A а также В лицо разделы
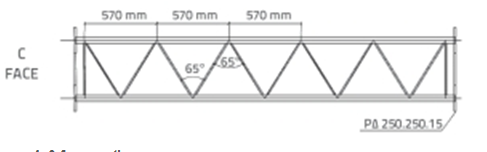
Фигура 4. С лицо раздел
Таблица 1. материал свойства
|
материал тип |
Растяжимый прочность [МПа] |
Урожай прочность [МПа] |
|
Ст52 (S355) |
510 |
360 |
Таблица 2. раздел свойства
|
член тип |
Раздел тип |
Размер [мм] |
|
колонка члены |
Трубка |
48×7 |
|
вертикальный члены |
круговое |
16 |
|
Диагональ члены |
круговое |
16 |
|
Члены парня |
круговое |
16 |
Таблица 3 Скорость ветра и нагрузки в зависимости от высоты
|
Высота [м] |
ветер скорость “v” [Миз] |
ветер нагрузка “Q” 2 [кг / м ] |
|
0-8 |
28 |
50 |
|
8-20 |
36 |
80 |
|
20-80 |
46 |
130 |
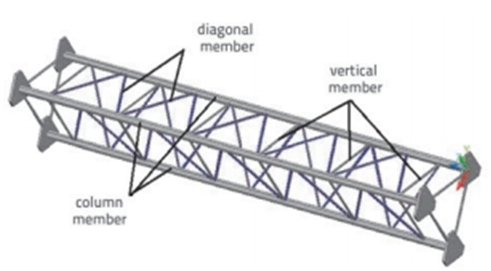
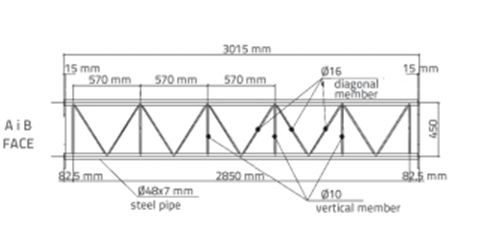
Модуль 3015 длиной мм изготовлен из стальных элементов. Колонны располагаются под углом 900 на землю. Вертикальные стальные элементы соединяют колонны друг с другом., и располагаются вертикально относительно колонн. Диагональные элементы располагаются под определенными углами к колоннам., а еще они соединяют колонны друг с другом. Колонна с диагональными и вертикальными элементами, составляющими модуль., показаны на рисунке 5.
Фигура 5. модуль члены
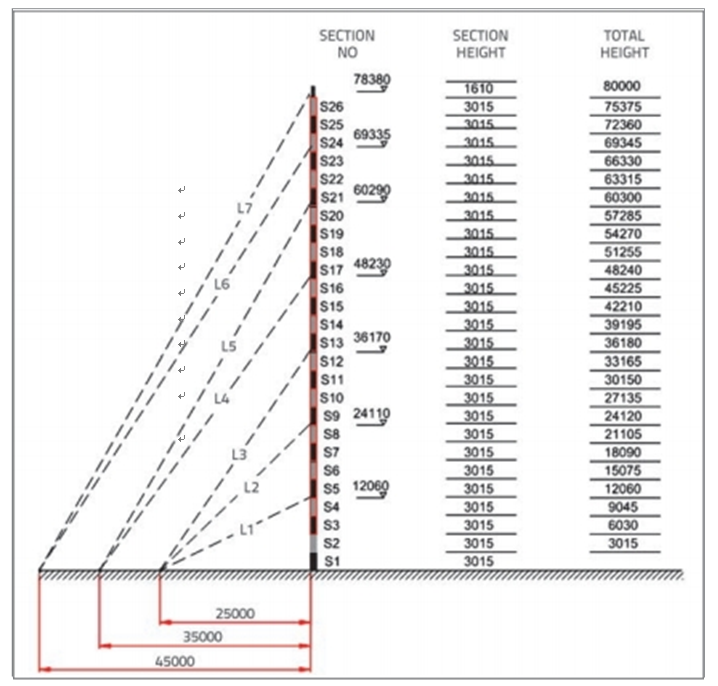
Оттяжки и модули названы по общей высоте от уровня земли.. Парень и номера разделов, с соответствующей высотой, представлены на рисунке 6.
Таблица 4. Высота и снегоуборочные свойства
|
высота над уровнем моря [м] |
Снег область, край |
Снег нагрузка Qs 2 [кг / м ] |
|
1500 |
IV |
176 |
Таблица 5. лед свойства
|
вес из единица измерения объем [кН / mm³ ] |
|
7 |
Есть 26 модули в решетке мачте. Колонка, вертикальный,и диагональные элементы в каждой грани модуля являются shownin Рис 7. Положительные и отрицательные направления ветра, влияющие на
Модуль также представлены на рисунке.

Таблица 6 раздел свойства
|
член |
Раздел тип |
Раздел размер [мм] |
Раздел длина окружности [см] |
Раздел площадь 2 [см ] |
|
колонка |
Трубка |
48×7 |
15.08 |
9.02 |
|
вертикальный |
круговое |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
Диагональ |
круговое |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
парень |
круговое |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
колонка |
Трубка |
48×7 |
15.08 |
9.02 |
|
вертикальный |
круговое |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
Диагональ |
круговое |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
парень |
круговое |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
колонка |
Трубка |
48×7 |
15.08 |
9.02 |
|
вертикальный |
круговое |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
Диагональ |
круговое |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
парень |
круговое |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
колонка |
Трубка |
48×7 |
15.08 |
9.02 |
|
вертикальный |
круговое |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
Диагональ |
круговое |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
|
парень |
круговое |
16 |
5.03 |
2.01 |
Сочетания нагрузок, использованные в анализе, приведены в уравнении (1) и уравнение (2) следующее. Комбинации составляют Снеговые нагрузки., ледовые нагрузки в зависимости от толщины льда,
и ветровые нагрузки, действующие на различную высоту решетчатой мачты при скорости ветра, приведены в табл. 7.
|
член |
Снег нагрузка 2 [кг / м ] |
распределенный снег нагрузка [кг / м] |
лед толщина [мм] |
распределенный лед нагрузка [кг / м] |
ветер скорость [км / ч] |
ветер нагрузка согласно в высота [кг / м] |
||
|
0-8 м |
8-20 м |
20-80 м |
||||||
|
колонка |
176 |
- |
30 |
5.15 |
209 |
12.18 |
19.49 |
26.81 |
|
вертикальный член |
4.42 |
3.03 |
4.06 |
6.50 |
8.94 |
|||
|
Диагональ член |
4.42 |
3.03 |
4.06 |
6.50 |
8.94 |
|||
|
парень |
4.42 |
3.03 |
4.06 |
6.50 |
8.94 |
|||
|
колонка |
176 |
- |
20 |
2.99 |
217 |
12.63 |
20.21 |
27.79 |
|
вертикальный член |
4.42 |
1.58 |
4.21 |
6.74 |
9.26 |
|||
|
Диагональ член |
4.42 |
1.58 |
4.21 |
6.74 |
9.26 |
|||
|
парень |
4.42 |
1.58 |
4.21 |
6.74 |
9.26 |
|||
|
колонка |
176 |
- |
10 |
1.28 |
223 |
12.96 |
20.73 |
28.50 |
|
вертикальный член |
4.42 |
0.57 |
4.32 |
6.91 |
9.50 |
|||
|
Диагональ член |
4.42 |
0.57 |
4.32 |
6.91 |
9.50 |
|||
|
парень |
4.42 |
0.57 |
4.32 |
6.91 |
9.50 |
|||
|
колонка |
176 |
- |
0 |
- |
226 |
13.14 |
21.03 |
28.92 |
|
вертикальный член |
4.42 |
- |
4.38 |
7.01 |
9.64 |
|||
|
Диагональ член |
4.42 |
- |
4.38 |
7.01 |
9.64 |
|||
|
парень |
4.42 |
- |
4.38 |
7.01 |
9.64 |
|||
Эффекты нагрузки боковых элементов. Распределенная снеговая нагрузка рассчитывается с учетом площади поверхности верхней членов.
Похожие сообщения
Башня связи — это тип башни передачи сигнала., также известная как башня передачи сигнала или железная башня связи. При строительстве современных вышек связи и передачи радио- и телесигнала., независимо от того, выбирают ли пользователи железные башни на уровне земли или на крыше, все они играют роль в поднятии антенн связи, увеличение радиуса обслуживания сигналов связи или телепередачи, и достижения идеальных специализированных коммуникационных эффектов. К тому же, крыша также играет двойную роль в заземлении молниезащиты., предупреждение о маршруте, и отделка офисных зданий.









